PREVNAR 20
(Pneumococcal 20-valent Conjugate Vaccine [Diphtheria CRM197 Protein])
Find PREVNAR 20 medical information:
Find PREVNAR 20 medical information:
PREVNAR 20 Quick Finder
Note: the information below includes the Part I: Health Professional Information.
1 Indications
Infants, Children and Adolescents (6 Weeks Through 17 Years of Age)
PREVNAR 20 (Pneumococcal 20-valent Conjugate Vaccine [Diphtheria CRM197 Protein]) is indicated for active immunization of infants, children and adolescents from 6 weeks through 17 years of age (prior to the 18th birthday) for the prevention of invasive pneumococcal disease (including sepsis, meningitis, bacteremic pneumonia, pleural empyema and bacteremia) caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 8, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 18C, 19A, 19F, 22F, 23F, and 33F.
Adults (18 Years of Age and Older)
PREVNAR 20 is indicated for active immunization of adults 18 years of age and older for the prevention of pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal disease (including sepsis, meningitis, bacteremic pneumonia, pleural empyema and bacteremia) caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 8, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 18C, 19A, 19F, 22F, 23F, and 33F.
Clinical efficacy for the prevention of pneumonia was studied with PREVNAR 13 for the shared serotypes (see 14 Clinical Trials), but not for the additional serotypes 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F.
PREVNAR 20 may not prevent disease caused by S. pneumoniae serotypes that are not contained in the vaccine.
1.1. Pediatrics
Based on the data submitted to and reviewed by Health Canada, the safety and efficacy of PREVNAR 20 in pediatric patients (6 weeks to <18 years of age) have been established. Therefore, Health Canada has authorized an indication for pediatric use in individuals 6 weeks through 17 years of age (prior to the 18th birthday). See 1 Indications, 8.2.1 Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions – Pediatrics and 14 Clinical Trials.
1.2. Geriatrics
PREVNAR 20 has been studied in the geriatric population (see 7.1 Special Populations and 14 Clinical Trials).
2 Contraindications
PREVNAR 20 is contraindicated in individuals who are hypersensitive to the active substance or to any component of the vaccine, including diphtheria toxoid. For a complete listing see 6 Dosage Forms, Strengths, Composition, and Packaging.
4 Dosage and Administration
4.1 Dosing Considerations
- Individuals at higher risk of pneumococcal infection, including patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, and those previously vaccinated with one or more doses of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23), are recommended to receive at least one dose of PREVNAR 20 (see 7 Warnings and Precautions, Immune and 14 Clinical Trials, PREVNAR 13 Immune Responses in Special Populations).
- In individuals with a hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), the recommended immunization series with PREVNAR 20 consists of four doses of 0.5 mL. The primary series consists of three doses, with the first dose given 3 to 6 months after HSCT and with an interval of at least 1 month between doses. A booster dose is recommended 6 months after the third dose (see 7 Warnings and Precautions, Immune and 14 Clinical Trials, PREVNAR 13 Immune Responses in Special Populations).
- If the sequential use of PPSV23 is considered appropriate, PREVNAR 20 should be given first.
4.2 Recommended Dose and Dosage Adjustment
4.2.1 Pediatrics (6 Weeks Through 17 Years of Age)
It is recommended that infants who receive a first dose of PREVNAR 20 complete the vaccination series with PREVNAR 20.
Routine Vaccination Schedule for Infants and Toddlers 6 Weeks Through 15 Months of Age
4-Dose Series (3-Dose Primary Series Followed by a Toddler Dose)
The vaccination series consists of 4 doses of PREVNAR 20, each of 0.5 mL. The primary series consists of 3 doses, with the first dose usually given at 2 months of age (and as early as 6 weeks of age), with an interval of 4 to 8 weeks between doses. The fourth dose should be given between 11 and 15 months of age and at least 2 months after the third dose.
See 14.2.2 Clinical Trials in Infants, Children and Adolescents 6 Weeks Through 17 Years of Age for the 3-Dose Series (2-Dose Primary Series Followed by a Toddler Dose)
Pre-term Infants (<37 Weeks Gestation at Birth)
The recommended vaccination series consists of 4 doses of PREVNAR 20, each of 0.5 mL. The primary series consists of 3 doses, with the first dose usually given at 2 months of age (and as early as 6 weeks of age), with an interval of 4 to 8 weeks between doses. The fourth dose should be given between 11 and 15 months of age and at least 2 months after the third dose.
Catch-up Vaccination Schedule for Unvaccinated Children and Adolescents 7 Months Through 17 Years of Age
Children 7 months through 17 years of age who have never received a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine may receive PREVNAR 20 according to the following schedules:
Infants 7 Through 11 Months of Age
Three doses of 0.5 mL, with the first 2 doses given at least 4 weeks apart. The third dose is given after the 1-year birthday, separated from the second dose by at least 2 months.
Children 12 Through 23 Months of Age
Two doses of 0.5 mL, with an interval of 2 months between doses.
Children and Adolescents 2 Through 17 Years of Age
One single 0.5 mL dose.
Catch-up Vaccination Schedule for Children Previously or Incompletely Vaccinated with PREVNAR 13
Children 15 months through 17 years of age who are considered completely immunized or with an incomplete vaccine series of PREVNAR 13 may receive 1 single 0.5 mL dose of PREVNAR 20. The catch-up (supplemental) dose of PREVNAR 20 should be administered with an interval of at least 8 weeks after the final dose of PREVNAR 13.
4.2.2 Adults (18 Years of Age and Older)
PREVNAR 20 is administered intramuscularly as a single 0.5 mL dose.
4.4 Administration
Do not mix PREVNAR 20 with any other vaccines or products in the same syringe.
Preparation for administration
Step 1. Vaccine resuspension Hold the pre-filled syringe horizontally between the thumb and the forefinger and shake vigorously until the contents of the syringe are a homogeneous white suspension. Do not use the vaccine if it cannot be re‑suspended. | 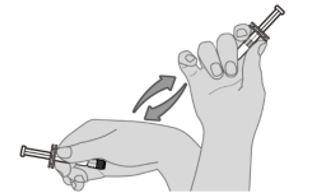 |
Step 2. Visual inspection Visually inspect the vaccine for large particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if large particulate matter or discoloration is found. If the vaccine is not a homogeneous white suspension, repeat steps 1 and 2. | 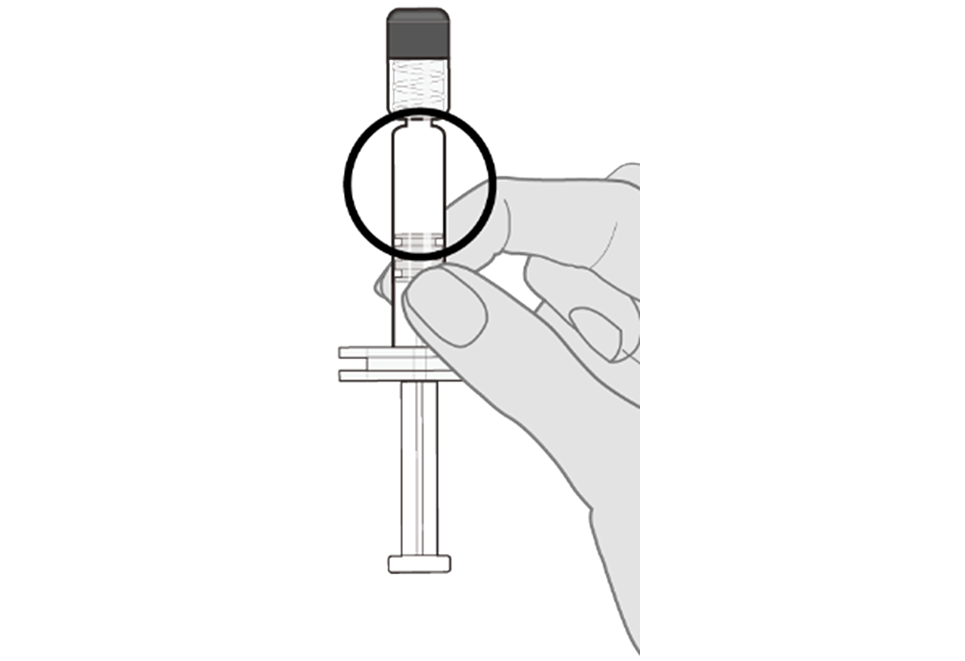 |
Step 3. Remove syringe cap Remove the syringe cap from the Luer lock adapter by slowly turning the cap counter‑clockwise while holding the Luer lock adapter.
Note: Care should be taken to ensure that the extended plunger rod is not depressed while removing the syringe cap. | 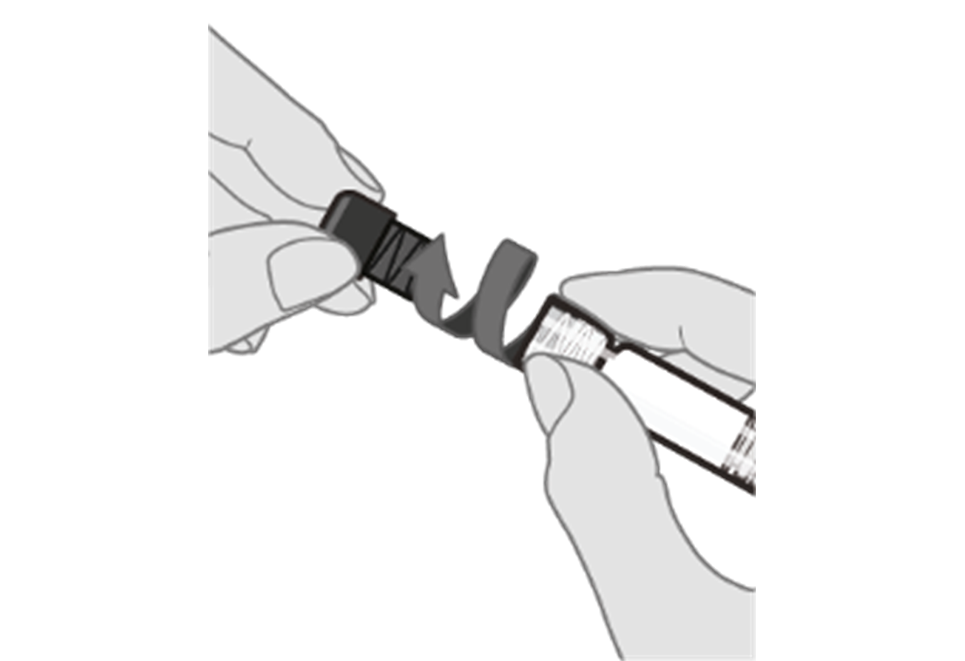 |
Step 4. Attach a sterile needle Attach a needle appropriate for intramuscular administration to the pre-filled syringe by holding the Luer lock adapter and turning the needle clockwise. | |
Administration
For intramuscular use only.
Each 0.5 mL dose is to be injected intramuscularly, with care to avoid injection into or near nerves and blood vessels. The preferred sites for injection are the anterolateral aspect of the thigh in infants and the deltoid muscle of the upper arm in children and adults. The vaccine should not be injected in the gluteal area.
Do not administer PREVNAR 20 intravascularly.
5 Overdose
Overdose with PREVNAR 20 is unlikely due to its presentation as a pre-filled syringe.
For the most recent information in the management of a suspected drug overdose, contact your regional poison control centre or Health Canada’s toll-free number, 1-844 POISON-X (1-844-764-7669).
6 Dosage Forms, Strengths, Composition and Packaging
PREVNAR 20 is a homogeneous white suspension for intramuscular injection supplied in a single-dose pre-filled syringe. Each 0.5 mL dose of the vaccine is formulated to contain approximately 2.2 mcg of each of S. pneumoniae serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 7F, 8, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 18C, 19A, 19F, 22F, 23F and 33F saccharides, 4.4 mcg of 6B saccharide, 51 mcg CRM197 carrier protein, 100 mcg polysorbate 80, 295 mcg succinic acid, 4.4 mg sodium chloride, and 125 mcg aluminum as aluminum phosphate adjuvant.
PREVNAR 20 is supplied in cartons of 1 and 10 single-dose pre-filled syringes, without needles.
The tip cap and plunger stopper of the pre‑filled syringe are not made with natural rubber latex.
| Route of Administration | Dosage Form / Strength / Composition | Non-medicinal Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Intramuscular | Suspension for injection 0.5 mL single-dose syringe | Aluminum phosphate Polysorbate 80 Sodium chloride Succinic acid Water for injection |
To help ensure the traceability of vaccines for patient immunization record-keeping as well as safety monitoring, health professionals should record the time and date of administration, quantity of administered dose (if applicable), anatomical site and route of administration, brand name and generic name of the vaccine, the product lot number and expiry date.
Description
A white suspension for intramuscular injection, provided in a single-dose (0.5 mL), pre-filled syringe.
7 Warnings and Precautions
General
As with all injectable vaccines, appropriate medical treatment and supervision must always be readily available in case of a rare anaphylactic event following the administration of the vaccine.
As with other vaccines, the administration of PREVNAR 20 should be postponed in individuals suffering from acute severe febrile illness. However, the presence of a minor infection, such as a cold, should not result in the deferral of vaccination.
PREVNAR 20 will only protect against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes included in the vaccine, and will not protect against other microorganisms that cause invasive disease or pneumonia.
As with any vaccine, PREVNAR 20 may not protect all individuals receiving the vaccine from pneumococcal disease.
Driving and Operating Machinery
PREVNAR 20 has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines. However, some of the effects mentioned under 8 Adverse Reactions may temporarily affect the ability to drive or use machines.
Hematologic
As with all injectable vaccines, the vaccine must be administered with caution to individuals with thrombocytopenia or a bleeding disorder since bleeding may occur following an intramuscular administration.
Immune
Safety and immunogenicity data on PREVNAR 20 are not available for individuals in immunocompromised groups and vaccination should be considered on an individual basis. Studies in individuals with HIV, sickle cell disease and bone marrow transplant have not been conducted with PREVNAR 20; however, safety and immunogenicity studies with PREVNAR 13 are relevant to PREVNAR 20, since the vaccines are manufactured similarly and contain 13 of the same polysaccharide conjugates (see 14 Clinical Trials).
Based on experience with pneumococcal vaccines, some individuals with altered immunocompetence may have reduced immune responses to PREVNAR 20. Individuals with impaired immune responsiveness, whether due to the use of immunosuppressive therapy, a genetic defect, HIV infection, or other causes, may have reduced antibody response to active immunization. The clinical relevance of this is unknown.
Reproductive Health
- Fertility
No human data on the effect of PREVNAR 20 on fertility are available.
Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to female fertility or reproductive toxicity (see 16 Non-Clinical Toxicology).
7.1. Special Populations
7.1.1. Pregnancy
Safety during pregnancy has not been established in humans.
7.1.2 Breastfeeding
Safety during lactation has not been established in humans.
It is not known whether vaccine antigens or antibodies are excreted in human milk.
7.1.3. Pediatrics
As with all injectable pediatric vaccines, the potential risk of apnea should be considered when administering the primary immunization series to preterm infants. The need for monitoring for at least 48 hours after vaccination should be considered for every preterm infant born ≤28 weeks of gestation who remains hospitalized at the time of the recommended administration. As the benefit of vaccination is high in this group of infants, vaccination should not be withheld or delayed.
The effectiveness of PREVNAR 20 for the prevention of pneumonia has not been established in individuals younger than 18 years of age.
The safety and effectiveness of PREVNAR 20 in children younger than 6 weeks of age have not been established.
7.1.4 Geriatrics
Of the 4,263 adults in the three Phase 3 studies of the clinical development program who received PREVNAR 20, 668 (15.7%) were 65 through 69 years of age, 398 (9.3%) were 70 through 79 years of age, and 72 (1.7%) were 80 years of age and older. PREVNAR 20 has been shown to be safe and immunogenic in the geriatric population regardless of prior pneumococcal vaccination (see 14 Clinical Trials).
8 Adverse Reactions
8.1. Adverse Reaction Overview
Adults 18 Years of Age and Older
The safety profile is based on the analysis of three Phase 3 clinical trials (see 14 Clinical Trials). There were 4,263 adult participants who received PREVNAR 20, which included 3,639 adults that were naïve to pneumococcal vaccines, 253 that had previously received the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, (Pneumovax® 23 [PPSV23]) only, 246 that had previously received PREVNAR 13 only, and 125 that had previously received both PPSV23 and PREVNAR 13. The most commonly reported solicited adverse reactions (>10%) were vaccination-site pain/tenderness, muscle pain, fatigue, headache and joint pain. Overall, the serious adverse events (SAEs) reported were consistent with diseases and conditions observed in adults of different age groups, and none were considered to be related to the study vaccine. In all three Phase 3 trials, PREVNAR 20 demonstrated a tolerability and safety profile similar to that of PREVNAR 13.
Infants, Children and Adolescents 6 Weeks Through 17 Years of Age
The safety of PREVNAR 20 was evaluated in 5,987 participants 6 weeks through 17 years of age in four randomized, double-blind, active-controlled clinical trials and one single-arm clinical trial (one Phase 2 and four Phase 3 trials); 3,664 participants received at least 1 dose of PREVNAR 20, and 2,323 participants received PREVNAR 13 (control vaccine). Across all 5 trials, there were similar percentages of male and female participants among the PREVNAR 20 recipients and the PREVNAR 13 recipients. Overall, 83.5% of PREVNAR 20 recipients were White, 7.9% Black, 1.6% Asian, and 24.0% Hispanic, with similar distribution among PREVNAR 13 recipients.
Infants and Children 6 Weeks to <15 Months of Age
Clinical trials were conducted in healthy infants and children 6 weeks to <15 months of age using a 3-dose series (Phase 3 Study 1012) or a 4-dose series (Phase 3 Studies 1011 and 1013 and Phase 2 Study 1003). In these 4 infant trials 5,156 participants received at least 1 dose of vaccine: 2,833 received PREVNAR 20 and 2,323 received PREVNAR 13. Overall, approximately 90% of participants in each group received all doses through the study-specified toddler dose. In all studies, local reactions and systemic events were collected after each dose, and adverse events were collected from the first dose through 1 month after the last infant vaccination and from the toddler dose through 1 month after the toddler dose in all studies. Serious adverse events were evaluated through 1 month after the last dose in Study 1012 and 6 months after the last dose in Studies 1011, 1013, and 1003.
PREVNAR 20 was well tolerated when administered on a 3-dose and a 4-dose series in the infant study populations, with low rates of severe local reactions and systemic events, and most reactions resolving within 1 to 3 days. The percentages of participants with reactogenicity events after PREVNAR 20 were generally similar to those after PREVNAR 13. Based on the infant data, the most frequently reported local reactions and systemic events after any dose of PREVNAR 20 were irritability, drowsiness, and pain at injection site. In these studies, PREVNAR 13 was co-administered or permitted to be administered with certain routine pediatric vaccines (see 14.2.3 Concomitant Vaccine Administration).
Study 1012 was a double-blind, active-controlled Phase 3 trial, in which 601 healthy infants, 2 months (≥42 to ≤112 days) of age and born at >36 weeks of gestation received PREVNAR 20 in a 3-dose series. The most frequently reported adverse reactions (>10%) after any dose of PREVNAR 20 were irritability (71.0% to 71.9%), drowsiness/increased sleep (50.9% to 61.2%), pain at injection site (22.8% to 42.4%), decreased appetite (24.7% to 39.3%), redness at injection site (25.3% to 36.9%), swelling at injection site (21.4% to 29.8%) and fever of ≥38.0°C (8.9% to 24.3%). Most adverse reactions occurred within 1 to 2 days following vaccination and were mild to moderate in severity and of short duration (1 to 2 days).
Studies 1011, 1013 and 1003 were double-blind, randomized, active-controlled trials that included 2,232 healthy infants vaccinated with PREVNAR 20 in a 4-dose series. The most frequently reported adverse reactions (>10%) observed after any dose of PREVNAR 20 in infants were irritability (58.5% to 70.6%), drowsiness/increased sleep (37.7% to 66.2%), pain at injection site (32.8% to 45.5%), decreased appetite (23.0% to 26.4%), redness at injection site (22.6% to 24.5%) and swelling at injection site (15.1% to 17.6%). Most adverse reactions were mild or moderate following vaccination and severe reactions were reported infrequently. In Study 1013, the local reactions and systemic events in the preterm subgroup (111 infants born at 34 to <37 weeks of gestation) were similar to or lower than the term infants in the study. In the preterm subgroup the frequency of any reported local reaction (31.7% to 55.3% in the PREVNAR 20 group and 37.9% to 47.1% in the PREVNAR 13 group) and systemic event (65.0% to 85.5% in the PREVNAR 20 group and 59.4% to 77.4% in the PREVNAR 13 group) were similar after PREVNAR 20 and PREVNAR 13. Most adverse reactions occurred within 1 to 2 days following vaccination and were mild to moderate in severity and of short duration (1 to 3 days).
The frequency and severity of the adverse reactions in all infant clinical trials were generally similar in the PREVNAR 20 and PREVNAR 13 groups.
Children and Adolescents 15 Months through 17 Years of Age
In Phase 3 Study 1014, 831 participants 15 months through 17 years of age received a single dose of PREVNAR 20 in four age groups (209 participants 15 to <24 months of age; 216 participants 2 years to <5 years of age; 201 participants 5 years to <10 years age; and 205 participants 10 years to <18 years of age). The participants <5 years of age had received at least 3 prior doses of PREVNAR 13.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions (>10%) observed after any dose of PREVNAR 20 in participants <2 years of age were irritability (61.8%), pain at injection site (52.5%), drowsiness/ increased sleep (41.7%), redness at injection site (37.7%), decreased appetite (25.0%), swelling at injection site (22.1%) and fever ≥38.0°C (11.8%). In participants aged 2 years and older, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were pain at injection site (66.0% to 82.9%), muscle pain (26.5% to 48.3%), redness at injection site (15.1% to 39.1%), fatigue (27.8% to 37.2%), headache (5.6% to 29.3%), and swelling at injection site (15.6% to 27.1%). Most adverse reactions occurred within 1 to 2 days following vaccination and were mild to moderate in severity and of short duration (1 to 3 days).
8.2. Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions
Clinical trials are conducted under very specific conditions. The adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials, therefore, may not reflect the rates observed in practice and should not be compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug. Adverse reaction information from clinical trials may be useful in identifying and approximating rates of adverse drug reactions in real-world use.
Adults 18 Years of Age and Older
Solicited Adverse Reactions
The frequency of solicited adverse reactions in adults <65 years of age naïve to pneumococcal vaccination and in adults ≥65 years of age by prior pneumococcal vaccination status are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. Local adverse reactions (redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site) were prompted daily for 10 consecutive days after vaccination. Systemic adverse events (fever, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, and joint pain) were prompted daily for 7 days after vaccination.
In general, the median onset day for local reactions was between Day 1 (day of vaccination) to Day 2.5, and they resolved with a median duration of 1 to 2 days. The median onset day for most systemic events was generally between Day 1 to Day 3.5, and they resolved with a median duration of 1 to 2 days.
| Adverse Reactionb | Study 1007 60-64 Years of Age | Study 1007 50-59 Years of Age | Study 1007 and Study 1008 18-49 Years of Age | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PREVNAR 20 (Na=991) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=990) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=331) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=111) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=1791) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=355) % | |
| Local Reaction | ||||||
| Redness | 7.1 | 6.3 | 8.2 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 7.3 |
| Swelling | 8.0 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 10.8 | 9.1 | 9.9 |
| Pain at injection site | 61.6 | 59.2 | 72.5 | 69.4 | 79.2 | 77.7 |
| Systemic Event | ||||||
| Fever ≥38.0°C | 0.8 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Fever >40.0°C | 0.2 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 32.7 | 32.4 | 39.3 | 36.0 | 46.7 | 43.7 |
| Headache | 24.5 | 25.3 | 32.3 | 36.0 | 36.7 | 36.6 |
| Muscle pain | 42.8 | 39.8 | 49.8 | 49.5 | 62.9 | 64.8 |
| Joint pain | 12.2 | 14.5 | 15.4 | 20.7 | 16.2 | 15.2 |
a. N = number of participants with any e-diary data reported after vaccination. b. Local reactions solicited within 10 days after vaccination; systemic events solicited within 7 days after vaccination. | ||||||
| Adverse Reactionb | Study 1007 | Study 1006 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior Pneumococcal Vaccination Statusc | |||||||
| Naïve | PPSV23 | PREVNAR 13 | PREVNAR 13 & PPSV23 | ||||
PREVNAR 20 % | PREVNAR 13 % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=253) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=121) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=245) % | PPSV23 % | PREVNAR 20 % | |
| Local Reaction | |||||||
| Redness | 7.8 | 6.1 | 7.9 | 2.5 | 8.6 | 12.7 | 4.8 |
| Swelling | 6.6 | 7.3 | 9.9 | 6.6 | 9.4 | 14.3 | 4.0 |
| Pain at injection site | 43.6 | 44.0 | 50.2 | 43.0 | 61.2 | 56.3 | 52.8 |
| Systemic Event | |||||||
| Fever ≥38.0°C | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 1.6 | 0 |
| Fever >40.0°C | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 25.3 | 27.2 | 28.9 | 22.3 | 31.0 | 33.3 | 32.8 |
| Headache | 15.8 | 19.3 | 17.8 | 18.2 | 13.5 | 21.4 | 19.2 |
| Muscle pain | 31.9 | 32.3 | 32.0 | 31.4 | 33.9 | 46.0 | 37.6 |
| Joint pain | 13.4 | 12.0 | 6.7 | 10.7 | 11.8 | 15.9 | 16.8 |
a. N = number of participants with any e-diary data reported after vaccination. b. Local reactions solicited within 10 days after vaccination; systemic events solicited within 7 days after vaccination. c. Includes participants who previously received either PPSV23 ≥1 to ≤5 years before enrollment (PPSV23), PREVNAR 13 ≥6 months before enrollment (PREVNAR 13), or PREVNAR 13 followed by PPSV23 ≥1 year before enrollment (PREVNAR 13 and PPSV23) in the study. | |||||||
Safety with Concomitant Vaccine Administration in Adults
In Study 1004, the frequency of all solicited systemic ARs within 7 days following coadministration of PREVNAR 20 and influenza vaccine, adjuvanted (QIV) was numerically higher when coadministered compared to when given separately. Following the coadministration, the most frequently reported systemic ARs were fatigue (33.2%), followed by headache (21.9%), muscle pain (19.7%), and joint pain (13.3%), with most cases being mild to moderate (≤0.9% were severe) and having an onset time and duration similar to those following administration of PREVNAR 20 or influenza vaccine alone. Occurrence of fever was low in the coadministration group (1.5%), PREVNAR 20-only group (0.5%), and the influenza vaccine-only group (0.6%). No other difference in the safety profile between coadministration and separate administration for each of these vaccines alone was observed.
In study 1026, the frequency of all solicited systemic ARs (fatigue, headache, chills, muscle pain, and joint pain) except fever within 7 days after vaccination in the coadministration group was similar to that in the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine-only group but noticeably higher than that in the PREVNAR 20-only group. The most frequent systemic ARs in the coadministration group were fatigue (54.1%), followed by muscle pain (32.4%), headache (30.3%), chills (26.5%), and joint pain (26.5%). Fever (13.0%) and use of antipyretic or pain medication (34.6%) in the coadministration group were higher than those in both the PREVNAR 20-only group (1.1% and 15.1%, respectively), and the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine-only group (8.6% and 28.6%, respectively). The frequency of solicited ARs with moderate severity (33.0% for fatigue, 11.9% for headache, and 11.4% for joint pain) in the coadministration group was higher than that in both the PREVNAR 20-only group (12.4% for fatigue, 2.7% for headache, and 3.8% for joint pain), and the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine-only group (24.9% for fatigue, 7.6% for headache, and 9.7% for joint pain). No other apparent difference in the safety profile between the coadministration group, and the Prevnar 20-only group or the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine-only group was observed.
8.2.1. Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions - Pediatrics
Children 6 Weeks Through 17 Years of Age
Infants and Toddlers Receiving a Routine Vaccination Schedule
The percentages of infants and toddlers with solicited local reactions and systemic events that occurred within 7 days after each dose of PREVNAR 20 or PREVNAR 13 following a 3-dose or 4-dose series are shown in Tables 4 and 5, respectively.
Study 1012 (Table 4) evaluated a 3-dose series of either PREVNAR 20 or PREVNAR 13 with a first dose given at 42 to 112 days of age, a second dose approximately 2 months later, and the third dose at 11 to 12 months of age. Participants received concomitant vaccines at these visits (see 14.2.3 Concomitant Vaccine Administration).
Studies 1003, 1011 and 1013 evaluated a 4-dose series of either PREVNAR 20 or PREVNAR 13 given at approximately 2, 4, 6, and 12 to 15 months of age (12 months of age for Study 1003). Participants received concomitant vaccines at these visits (see 14.2.3 Concomitant Vaccine Administration). Table 5 presents pooled data from these 3 studies.
| Dose | Dose 1 | Dose 2 | Dose 3 (Toddler Dose) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PREVNAR 20 (Na=598) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=603) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=592) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=594) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=580) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=586) % | |
| Local Reaction | ||||||
Pain at injection sitec Any Moderate Severe |
29.1 12.0 0.3 |
29.4 11.4 0 |
22.8 9.3 0.2 |
24.6 7.9 0.2 |
42.4 17.4 0.3 |
39.9 17.2 0.3 |
Rednessb Any Moderate Severe |
25.3 4.5 0 |
27.5 4.8 0 |
28.5 3.7 0 |
28.1 5.1 0.2 |
36.9 13.4 0.2 |
33.8 8.5 0.2 |
Swellingb Any Moderate Severe |
21.4 8.7 0 |
20.2 7.3 0 |
22.0 8.3 0 |
20.5 6.2 0.2 |
29.8 11.9 0.2 |
24.6 9.7 0.3 |
| Systemic Event | ||||||
| Irritability | 71.9 | 72.5 | 71.6 | 68.4 | 71.0 | 70.8 |
| Drowsiness | 61.2 | 63.7 | 51.4 | 50.7 | 50.9 | 48.6 |
| Decreased appetite | 24.7 | 22.6 | 24.7 | 19.4 | 39.3 | 36.5 |
Fever Any (≥38.0°C) >38.9 to 40°C >40.0°C |
8.9 0 0 |
8.5 0.3 0 |
14.9 0.7 0 |
14.0 0.3 0 |
24.3 3.6 0.3 |
23.7 3.2 0 |
- N = number of participants with any e-diary data reported after vaccination. This value is the denominator for percentage calculations.
- Any: >0.0 cm; Moderate: >2.0 to 7.0 cm; severe: >7.0 cm.
- Any: any pain at injection site; Moderate: hurts if gently touched with crying; Severe: causes limitation of arm movement.
| Dose | Dose 1 | Dose 2 | Dose 3 | Dose 4 (Toddler Dose) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PREVNAR 20 (Na=2214) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=1696) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=2107) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=1613) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=2055) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=1582) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=1904) % | PREVNAR 13 (Na=1454) % | |
| Local Reaction | ||||||||
Pain at injection sitec Any Moderate Severe |
45.5 17.1 0.2 |
45.4 15.8 0 |
38.6 13.1 0.4 |
39.9 14.0 0.2 |
32.8 11.0 0.1 |
35.5 12.4 0 |
33.4 10.5 0.5 |
34.6 8.9 0 |
Rednessb Any Moderate Severe |
23.8 3.7 0 |
23.2 2.5 0 |
23.5 2.6 0 |
25.7 3.7 0 |
24.5 3.7 0 |
25.0 3.5 0.1 |
22.6 4.6 0.1 |
25.6 4.0 0 |
Swellingb Any Moderate Severe |
17.6 5.1 0.1 |
17.6 4.1 0 |
16.7 4.2 0 |
18.0 4.5 0 |
16.8 4.0 0 |
17.5 3.5 0.2 |
15.1 4.3 0 |
16.0 3.2 0 |
| Systemic Event | ||||||||
| Irritability | 70.6 | 71.5 | 68.4 | 69.9 | 60.8 | 61.4 | 58.5 | 59.4 |
| Drowsiness | 66.2 | 65.6 | 52.4 | 54.1 | 39.8 | 41.9 | 37.7 | 38.1 |
| Decreased appetite | 24.8 | 24.7 | 24.9 | 23.1 | 23.0 | 22.3 | 26.4 | 25.9 |
Fever Any(≥38.0°C) >38.9 to 40°C >40.0°C |
10.3 0.7 0 |
8.5 0.4 0 |
16.5 1.9 0.1 |
15.7 1.6 0 |
12.7 1.6 0 |
13.1 1.8 0 |
16.0 3.2 0.2 |
15.0 3.0 0.1 |
- N = number of participants with any e-diary data reported after vaccination. This value is the denominator for percentage calculations.
- Any: >0.0 cm; Moderate: >2.0 to 7.0 cm; severe: >7.0 cm.
- Any: any pain at injection site; Moderate: hurts if gently touched with crying; Severe: causes limitation of arm movement
Safety with Concomitant Vaccine Administration in Infants and Toddlers
The safety profile of PREVNAR 20 was acceptable, and similar to PREVNAR 13 when administered concomitantly with routine pediatric vaccines containing diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B virus, poliovirus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b antigens; measles, mumps, and rubella antigens; and varicella antigens (see 14.2.3 Concomitant Vaccine Administration).
Children 15 Months Through 17 Years of Age
Study 1014 evaluated the safety of a single dose of PREVNAR 20 in children 15 months through 17 years of age. The percentages of children (by age group) with solicited local reactions and systemic events that occurred within 7 days after a dose of PREVNAR 20 or PREVNAR 13 are shown in Table 6. The types of solicited systemic events collected in the participants 15 months to <2 years of age were consistent with those collected in infants, while the solicited systemic events in children ≥2 years of age required verbal communication by the participant.
| Age | 15 to <24 Months | 2 to <5 Years | 5 to <10 Years | 10 to <18 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PREVNAR 20 (Na=204) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=215) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=199) % | PREVNAR 20 (Na=205) % | |
| Local Reaction | ||||
Rednessb Any Moderate Severe |
37.7 7.4 0 |
39.1 15.3 0.9 |
37.2 18.6 2.0 |
3.9 0.5 |
Swellingb Any Moderate Severe |
22.1 6.4 0 |
23.3 11.2 0.5 |
27.1 15.6 1.0 |
15.6 10.2 0 |
Pain at injection sitec Any Moderate Severe |
52.5 9.8 1.0 |
66.0 17.7 1.4 |
82.9 24.6 1.5 |
82.0 17.6 1.5 |
| Systemic Eventd | ||||
Fever Any (≥38.0°C) >38.9 to 40°C >40.0°C |
11.8 2.9 0 |
3.3 0.5 0 |
0.5 0 0 |
0 0 0 |
| Decreased appetite | 25.0 | - | - | - |
| Drowsiness/increased sleep | 41.7 | - | - | - |
| Irritability | 61.8 | - | - | - |
| Fatigue | - | 37.2 | 28.1 | 27.8 |
| Headache | - | 5.6 | 18.6 | 29.3 |
| Muscle pain | - | 26.5 | 39.2 | 48.3 |
| Joint pain | - | 3.7 | 6.5 | 8.3 |
- N = number of participants with any e-diary data reported after vaccination. This value is the denominator for percentage calculations.
- Any: >0.0 cm; Moderate: >2.0 to 7.0 cm; severe: >7.0 cm.
- For participants 15 months to <24 months of age: Any: any pain at injection site; Moderate: hurts if gently touched with crying; Severe: causes limitation of arm movement. For participants 2 years to <18 years of age: Any: any pain at injection site; Moderate: interferes with activity; Severe: prevents daily activity.
- For participants 15 months to <24 months of age, solicited systemic events were fever, decreased appetite, drowsiness/increased sleep and irritability. For participants 2 years to <18 years of age, solicited systemic events were fever, fatigue, headache, muscle pain and joint pain.
8.2.2. Additional Information in Immunocompromised Patients in Studies with PREVNAR 13
Children and adolescents 6 through 17 years of age with SCD, HIV infection or HSCT who received PREVNAR 13 had similar frequencies of adverse reactions as children and adolescents 2 through 17 years of age who received PREVNAR 13, except vaccination-site pain causing limitation of limb movement, joint pain, fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue and muscle pain had a frequency category of very common (≥1/10).
Adults 18 years and older with HIV infection who received PREVNAR 13 had similar frequencies of adverse reactions as adults 18 years of age and older who received PREVNAR 13, except that fever and vomiting had a frequency category of Very Common (≥1/10) and nausea had a frequency category of Common (≥1/100 to <1/10).
Adults 18 years and older with a HSCT who received PREVNAR 13 had similar frequencies of adverse reactions as adults 18 years and older who received PREVNAR 13, except that fever, diarrhea and vomiting had a frequency category of Very Common (≥1/10).
8.3. Less Common Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions
Adults 18 Years of Age and Older
Listed below are the less common adverse reactions reported in adult clinical trials with PREVNAR 20 (Uncommon frequency ≥1/1,000 to <1/100).
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reaction, including face edema, dyspnea, bronchospasm
Gastrointestinal disorders: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, angioedema
General disorders and administration site conditions: Vaccination-site pruritus, lymphadenopathy, vaccination-site urticaria, chills
8.3.1. Less Common Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions - Pediatrics
Less common adverse reactions reported in children 6 weeks to <5 years of age in PREVNAR 20 pediatric clinical trials included vomiting (1.4%), diarrhea (1.0%), rash (1.0%), urticaria or urticaria-like rash (0.5%), seizures (including febrile seizures) (0.4%) and vaccination site hypersensitivity (<0.1%).
Less common adverse reactions reported in the PREVNAR 20 pediatric clinical in children 5 to <18 years of age included urticaria or urticaria-like rash (0.5%).
Additionally, as PREVNAR 20 contains the same 13 serotype-specific capsular polysaccharide conjugates and the same vaccine excipients as PREVNAR 13, the adverse reactions already identified and listed below for PREVNAR 13 have been adopted for PREVNAR 20. In clinical trials, the safety profile of PREVNAR 20 was similar to that of PREVNAR 13. The frequencies below are defined as follows: very common (≥10%), common (≥1% to <10%), uncommon (≥0.1% to <1%), and rare (≥0.01% to <0.1%). For the following adverse reactions reported only for PREVNAR 13 in clinical trials, but not also reported in PREVNAR 20 clinical trials, the frequency is unknown for PREVNAR 20.
Adverse reactions reported for infants and children 6 weeks to <5 years of age in PREVNAR 13 clinical trials:
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reaction, including face edema, dyspnea, bronchospasm (rare)
Nervous system disorders: Hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode (rare), restless sleep/decreased sleep (very common)
Psychiatric disorders: Crying (uncommon)
Adverse reactions reported for children and adolescents 5 years to <18 years of age in PREVNAR 13 clinical trials:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Diarrhea (common), vomiting (common)
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Decreased appetite (very common)
Nervous system disorders: Drowsiness/increased sleep (very common), restless sleep/decreased sleep (very common)
Psychiatric disorders: Irritability (very common)
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash (common)
8.5 Post-Market Adverse Reactions
Post-marketing Experience with PREVNAR 13
The following adverse reactions have been reported since market introduction of PREVNAR 13, and are included based on one or more of the following factors: severity, frequency of reporting, or strength of evidence for a causal relationship to PREVNAR 13. These adverse reactions reported in the post-marketing experience of PREVNAR 13 in pediatric and adult populations may also be seen in post-marketing experience with PREVNAR 20 as the components of PREVNAR 13 are also contained in PREVNAR 20.
| System Organ Class | Frequency Not Known |
|---|---|
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Lymphadenopathy localized to the region of the vaccination-site |
| Immune system disorders | Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction including shock |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Angioedema, erythema multiforme |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Vaccination-site dermatitis, vaccination-site pruritus, vaccination-site urticaria |
9 Drug Interactions
If PREVNAR 20 is administered at the same time as another injectable vaccine, the vaccines should always be administered with different syringes and given at different injection sites.
Do not mix PREVNAR 20 with other vaccines/products in the same syringe.
Adults
PREVNAR 20 can be administered concomitantly with influenza vaccine, adjuvanted quadrivalent (QIV) or with COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (see 14 Clinical Trials, Concomitant vaccine administration)
Infants and Children 6 Weeks To <5 Years of Age
In infants and children 6 weeks to <5 years of age, PREVNAR 20 can be administered concomitantly with any of the following vaccine antigens, either as monovalent or combination vaccines: diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae type b, inactivated poliomyelitis, hepatitis B, measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) and varicella vaccines. The vaccine has been safely administered with influenza and rotavirus vaccine.
There are no data on the concomitant administration of PREVNAR 20 with other vaccines.
10 Clinical Pharmacology
10.1 Mechanism of Action
S. pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is a gram-positive diplococcus that can cause invasive disease including meningitis, sepsis, and pneumonia with bacteremia and non-invasive disease such as pneumonia without bacteremia. Non-bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia accounts for the majority of pneumococcal disease cases among the adult population. Over 100 different serotypes of pneumococcus have been identified. The serotypes included in PREVNAR 20 were selected based on their relevance in causing global disease and have been associated with higher case fatality rates and mortality, antibiotic resistance, meningitis and outbreaks.
PREVNAR 20 contains 20 pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides all conjugated to CRM197 carrier protein, which modifies the immune response to the polysaccharide from a T cell independent response to a T cell dependent response. The T-cell dependent response leads to a higher antibody response, and induces antibodies that enhance opsonisation, phagocytosis and killing of pneumococci to protect against pneumococcal disease, as well as generation of memory B cells, allowing for an anamnestic (booster) response on re-exposure to bacterial polysaccharide. In the absence of T-cell help, plain polysaccharide (PS) stimulated B-cells predominantly produce IgM antibodies; there is generally no affinity maturation of the antibodies, and no memory B-cells are generated. As vaccines, PSs are associated with poor or absent immunogenicity in infants less than 24 months of age and failure to induce immunological memory at any age.
Immune responses in children and adults following natural exposure to S. pneumoniae or following pneumococcal vaccination can be determined by measuring opsonophagocytic activity (OPA) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) responses. OPA represents functional antibodies and is considered an important immunologic surrogate measure of protection against pneumococcal disease in adults. In children, multiple immunogenicity criteria are used for the clinical evaluation of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines including the IgG antibody level of 0.35 mcg/mL using the World Health Organization (WHO) enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or equivalent assay-specific value. The levels of circulating antibodies in adults and the serotype-specific IgG levels in pediatric populations that correlate with protection against pneumococcal disease have not been clearly defined.
11 Storage, Stability and Disposal
Store in a refrigerator between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Syringes should be stored in the refrigerator horizontally to minimize the re-dispersion time.
Do not freeze. Discard if the vaccine has been frozen.
PREVNAR 20 should be administered as soon as possible after being removed from refrigeration.
PREVNAR 20 can be administered provided total (cumulative multiple excursions) time out of refrigeration (at temperatures between 8°C and 25°C) does not exceed 96 hours.
Cumulative multiple excursions between 0°C and 2°C are also permitted as long as the total time between 0°C and 2°C does not exceed 72 hours. These are not, however, recommendations for storage.
12 Special Handling Instructions
During storage, a white deposit and clear supernatant may be observed in the pre-filled syringe containing the suspension. Syringes should be stored horizontally to minimize the re-dispersion time.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Control #: 299005
September 29, 2025
Resources
Didn’t find what you were looking for?
Contact us
*Contact Medical Information. 9AM-5PM ET Monday to Friday; excluding holidays.
Submit a medical question for Pfizer prescription products.
Report Adverse Event
Contact Pfizer Safety to report an adverse event, side effect or concern about the quality of a Pfizer product:
You may also contact the Canada Vigilance Program directly to report adverse events or product quality concerns at 1-866-234-2345 or www.healthcanada.gc.ca/medeffect.